TMS vs Ketamine: Which Depression Treatment Is Right for You?

When it comes to treating depression, patients are no longer limited to traditional medication. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) and Ketamine Therapy have both emerged as effective options for individuals struggling with treatment-resistant depression. But how do you know which one is right for you?
This guide breaks down the key differences between TMS and Ketamine - including how they work, what to expect, and when to consider each one.
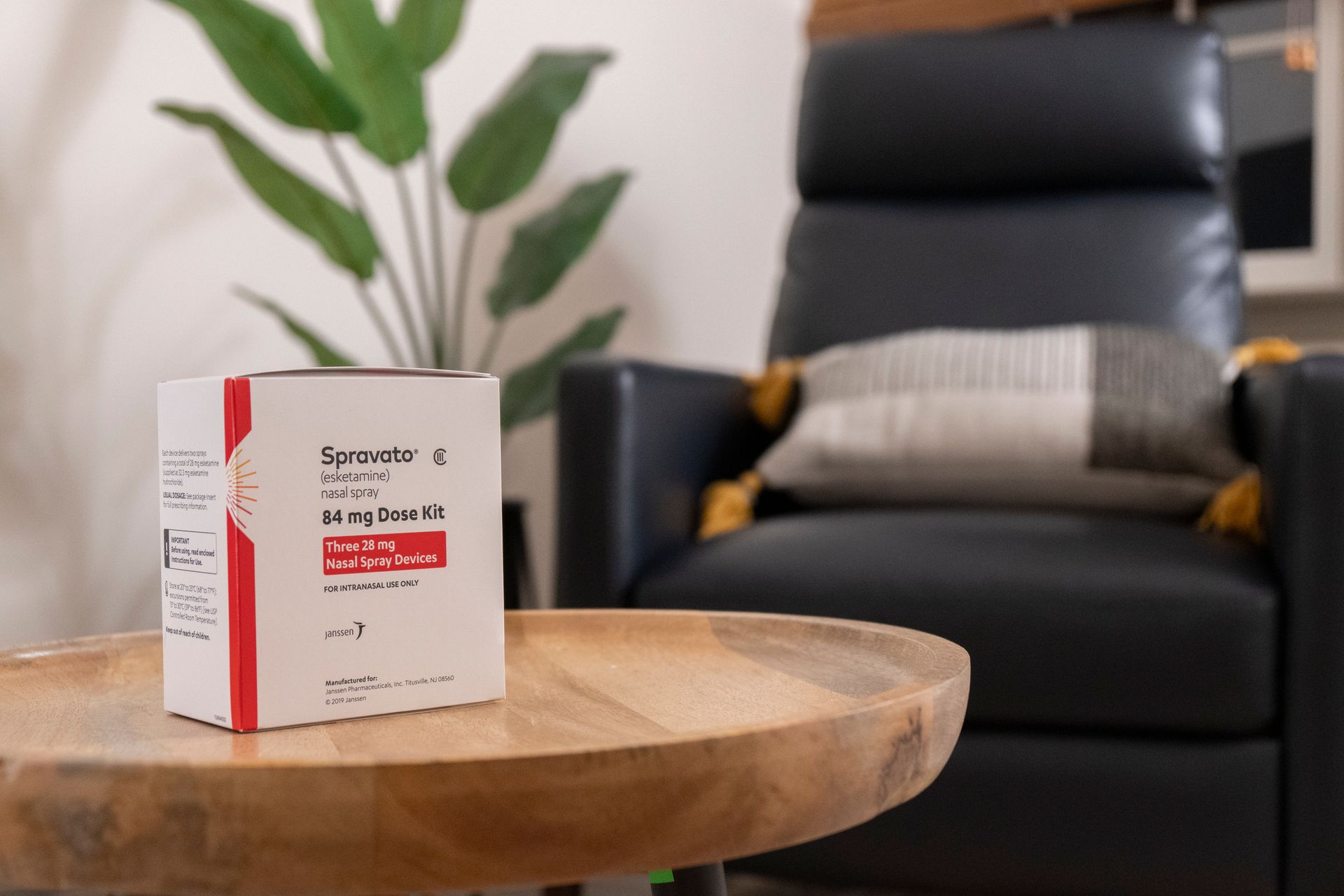
What Is Ketamine Therapy?
Once used primarily as an anesthetic (and later misused recreationally), Ketamine is now showing strong promise for individuals facing severe depression, anxiety, PTSD, and even suicidal thoughts. It works by quickly altering brain chemistry to improve mood - often within hours.
Ketamine Is Commonly Used For:
- Treatment-resistant depression
- Major depressive disorder
- Anxiety
- PTSD
- Addiction
- Suicidal ideation
How It’s Delivered:
- IV or IM infusions (most common)
- Nasal spray (e.g. Spravato)
- Oral formulations (less common)
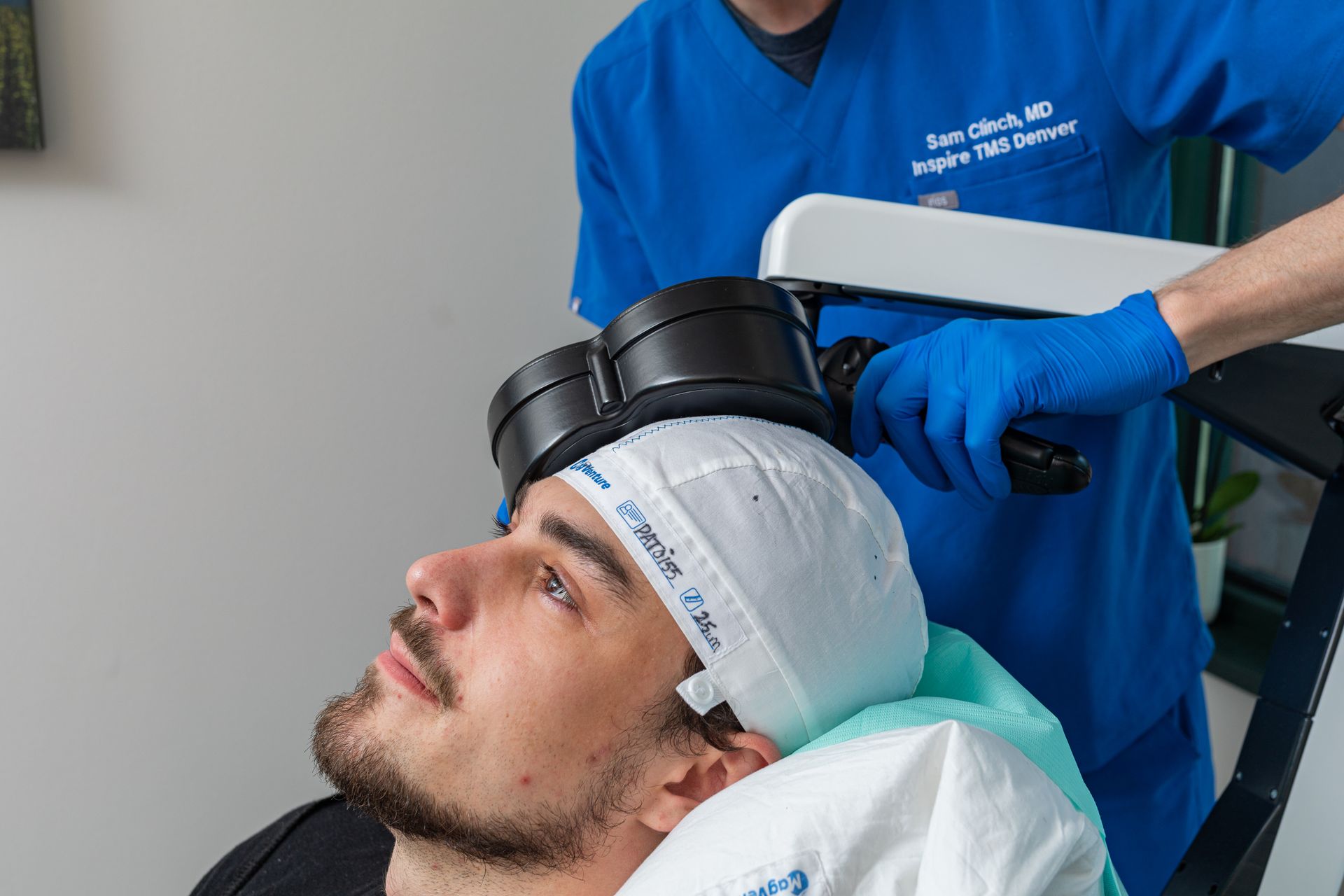
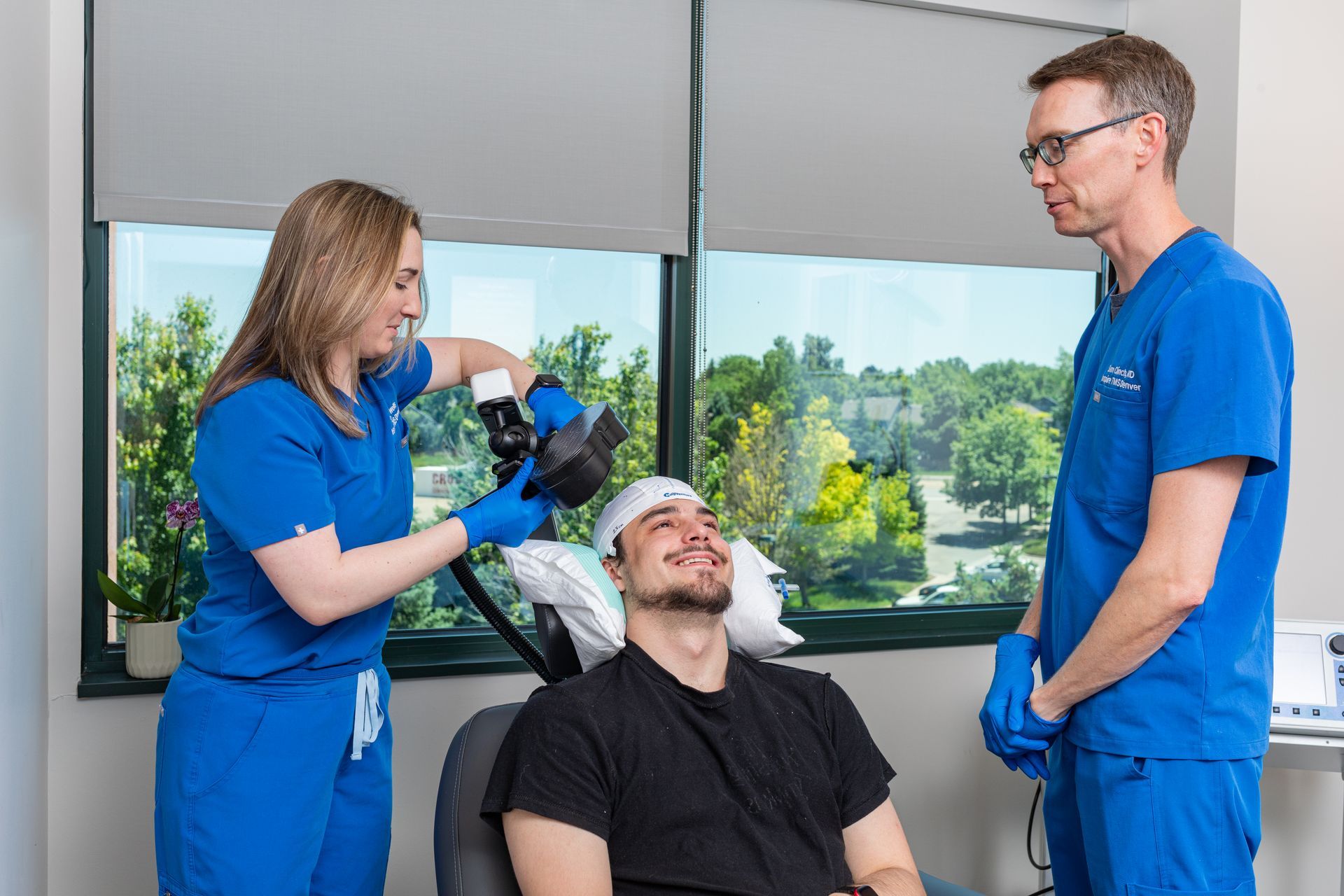
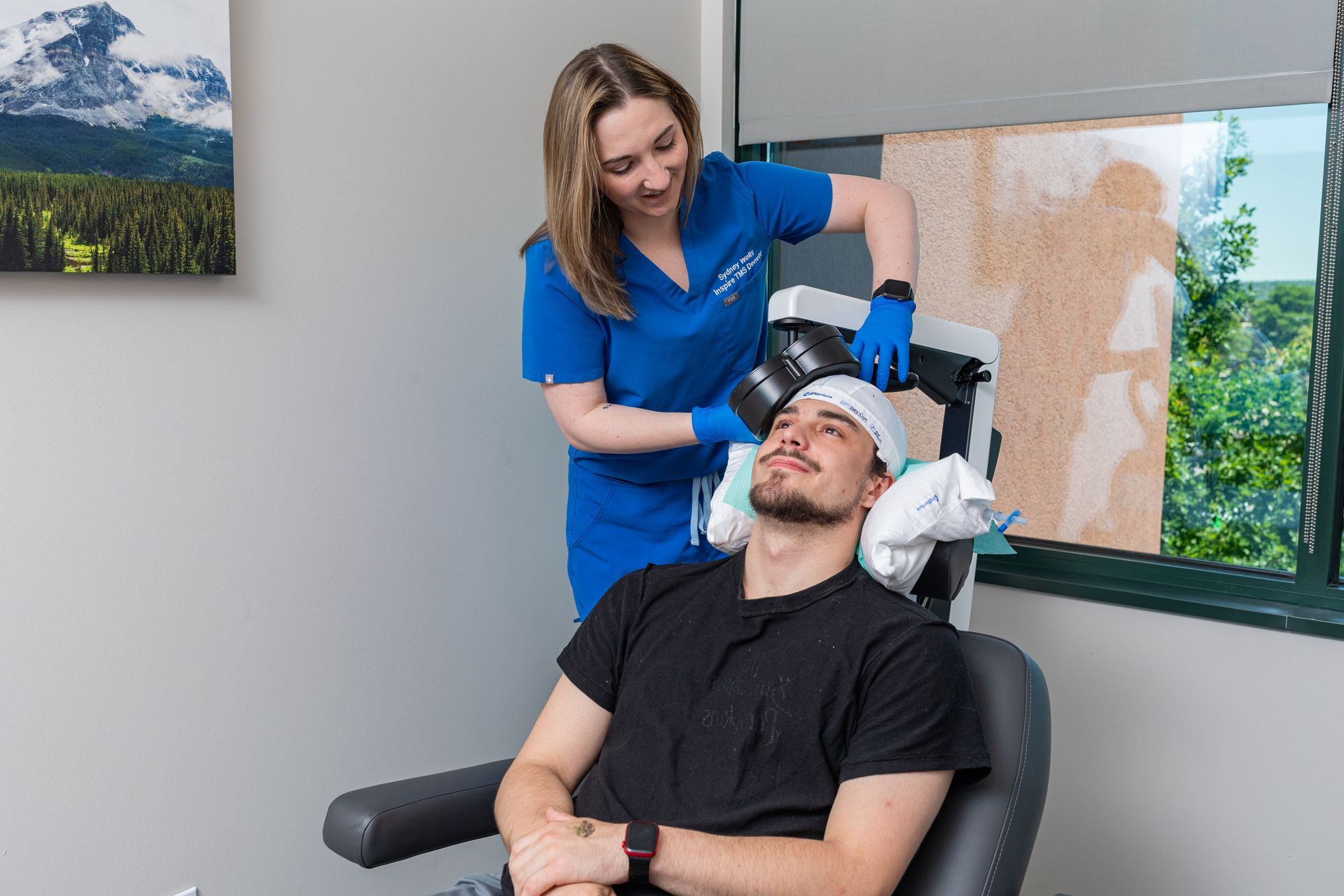
What Is TMS Therapy?
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is an FDA-approved, non-invasive treatment that uses magnetic pulses to stimulate parts of the brain linked to mood regulation. It’s ideal for patients who haven’t responded to medication or prefer drug-free solutions.
TMS Is Commonly Used For:
- Depression
- OCD
- Anxiety
- Postpartum depression
- Bipolar depression (off-label use)
TMS vs Ketamine: Key Differences
| Feature | Ketamine Therapy | TMS Therapy |
|---|---|---|
| Time to Effect | Often within hours | 2–4 weeks |
| Session Length | ~90 minutes | 3–30 minutes |
| Treatment Duration | 6–10 sessions (2–4 weeks) | 30–36 sessions (6 weeks) |
| Maintenance | Booster every 2–4 weeks | Optional 2/month for 12 months |
| Response Rate | ~70% after 6 infusions | ~70% after full course |
| FDA Approval | Approved for anesthesia only | Approved for depression, OCD, smoking cessation |
| Insurance Coverage | Limited / out of pocket | Widely covered by major insurers |
| Side Effects | Dissociation, nausea, tremors | Headache, scalp sensitivity |
| During Pregnancy | Not recommended | Considered safe |
How Do They Feel?
During Ketamine:
Patients describe sensations like relaxation, euphoria, altered perception, and deep emotional release. Clinical staff monitor vitals throughout treatment.
During TMS:
You sit comfortably in a chair while a device delivers gentle magnetic pulses. Some describe it as a light tapping sensation on the head. No sedation or recovery time needed.
Which Is Right for You?
Choose Ketamine if you:
- Need fast-acting symptom relief
- Struggle with suicidal ideation
- Haven’t responded to other treatments
Choose Ketamine if you:
- Prefer a non-drug option
- Want long-term results with minimal side effects
- Have tried antidepressants without success
Still not sure? Take our quiz to see if TMS is right for you
Final Thoughts
Both TMS and Ketamine are promising treatments for depression, but they work in very different ways. Consulting with a provider who offers both - or who understands how they compare - is the best way to make an informed decision.
At Inspire TMS Denver, we specialize in FDA-approved TMS therapy with proven results and personalized care. Want to learn more about your options?

Every Question Answered
Want to know more about TMS? Check out this in-depth guide to TMS therapy with transparent and easy to understand explanations about TMS processes, protocols, and treated conditions.
Latest Posts